Center for Multi-Messenger Astrophysics
Welcome to the Center for Multimessenger Astrophysics
The Center for Multimessenger Astrophysics (Formerly Center for Particle and Gravitational Astrophysics) is engaged in a bold synergistic approach to understanding high energy processes in the universe. Our faculty at Penn State are prominent participants in eight major international projects which make observations using extremely high energy protons and nuclei, neutrinos, gamma-rays, X-rays and gravitational waves. These projects are, respectively, the Pierre Auger Cosmic Ray Observatory, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Explorer satellite, the Chandra X-ray Observatory, the XMM-Newton X-ray Observatory, the Laser Interferometric Gravitational Wave Observatory (LIGO), the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational-waves (NANOGrav) and the High Altitude Water Cherenkov (HAWC) TeV gamma-ray detector.
Our faculty are also involved in developing instrumentation for future facilities such as the International X-ray Observatory, the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) and a major ESA flagship mission, the X-ray observatory Athena. There is also ongoing work with the Fermi satellite, the VERITAS high energy gamma ray observatory, the Cosmic Ray Energetics and Mass (CREAM), including a version to deploy on the International Space Station (ISS-CREAM), the High Energy Light Isotope eXperiment (HELIX) high-altitude balloon, and in the former Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) project, now called NGO.
Penn State is one of only a small handful of U.S. institutions participating in both Auger and IceCube, the premier ground-based projects of high energy particle astrophysics. Potentially observable sources for both Auger and IceCube include super-massive black holes at the center of active galaxies, and the explosive phenomena that give rise to gamma ray bursts (GRBs). Some GRBs are believed to be especially violent supernova explosions, while others are probably mergers of collapsed stars in binary systems.
The Swift GRB Explorer satellite is presently providing the best gamma ray and X-ray observations of GRB explosions. Swift has been successfully operating for a number of years, its mission control center being at Penn State. Chandra and XMM have been successfully operating for over a decade and are leading to substantial advances in understanding the demography, physics, and ecology of supermassive and stellar mass black holes, active galaxies and supernovae. The Advanced LIGO (aLIGO) gravitational wave detector has chalked up its first major success in making the first direct detection of gravitational waves, originating from 60 solar mass black hole binary system.
Commensurate with these significant experimental efforts, Penn State also plays a leading role in the theoretical and numerical modeling of fundamental high energy interactions as well as astrophysical phenomena such as black holes, gamma-ray bursts, the high energy Universe and the formation of the first objects and large scale structures in the Universe.
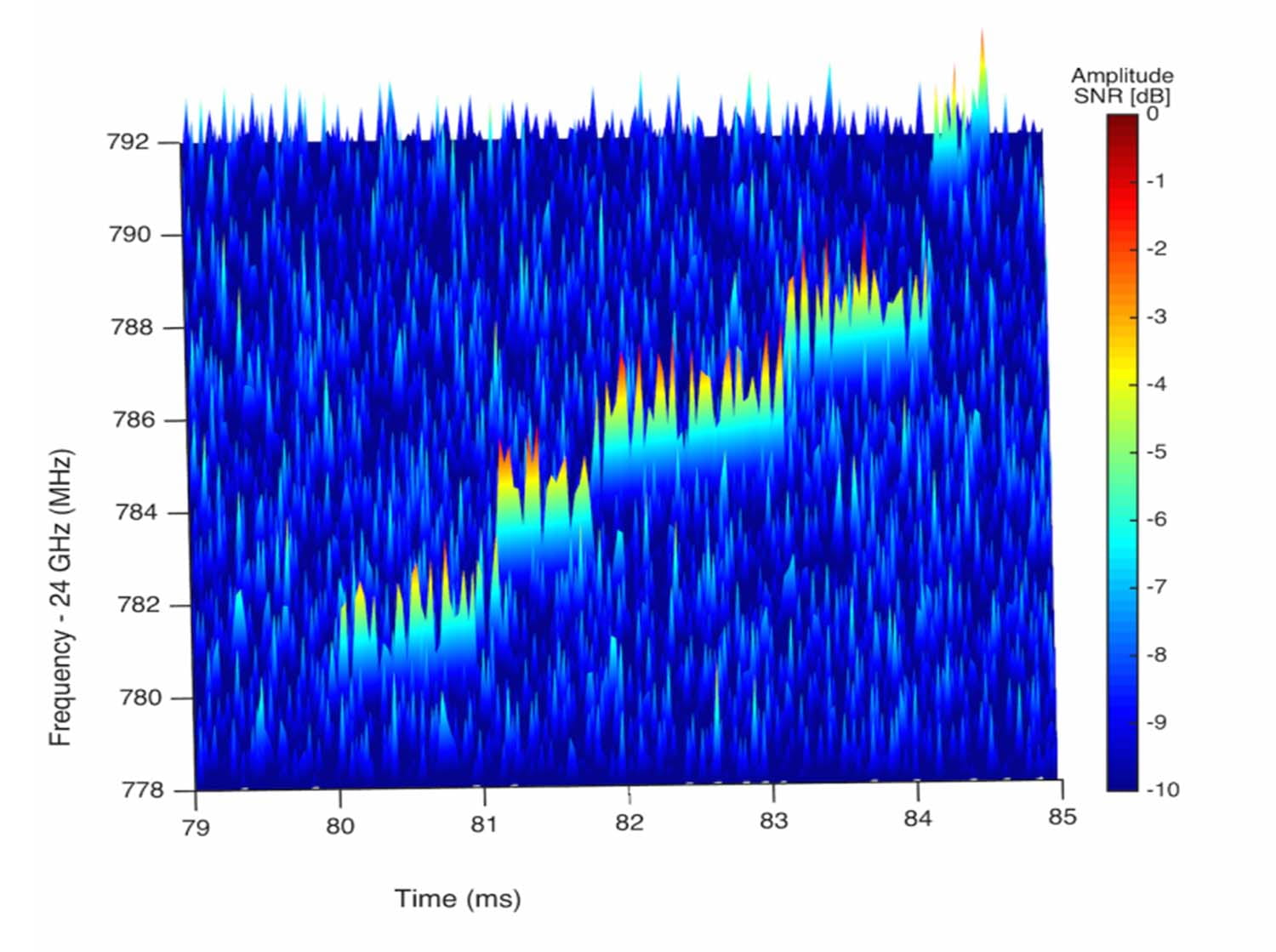
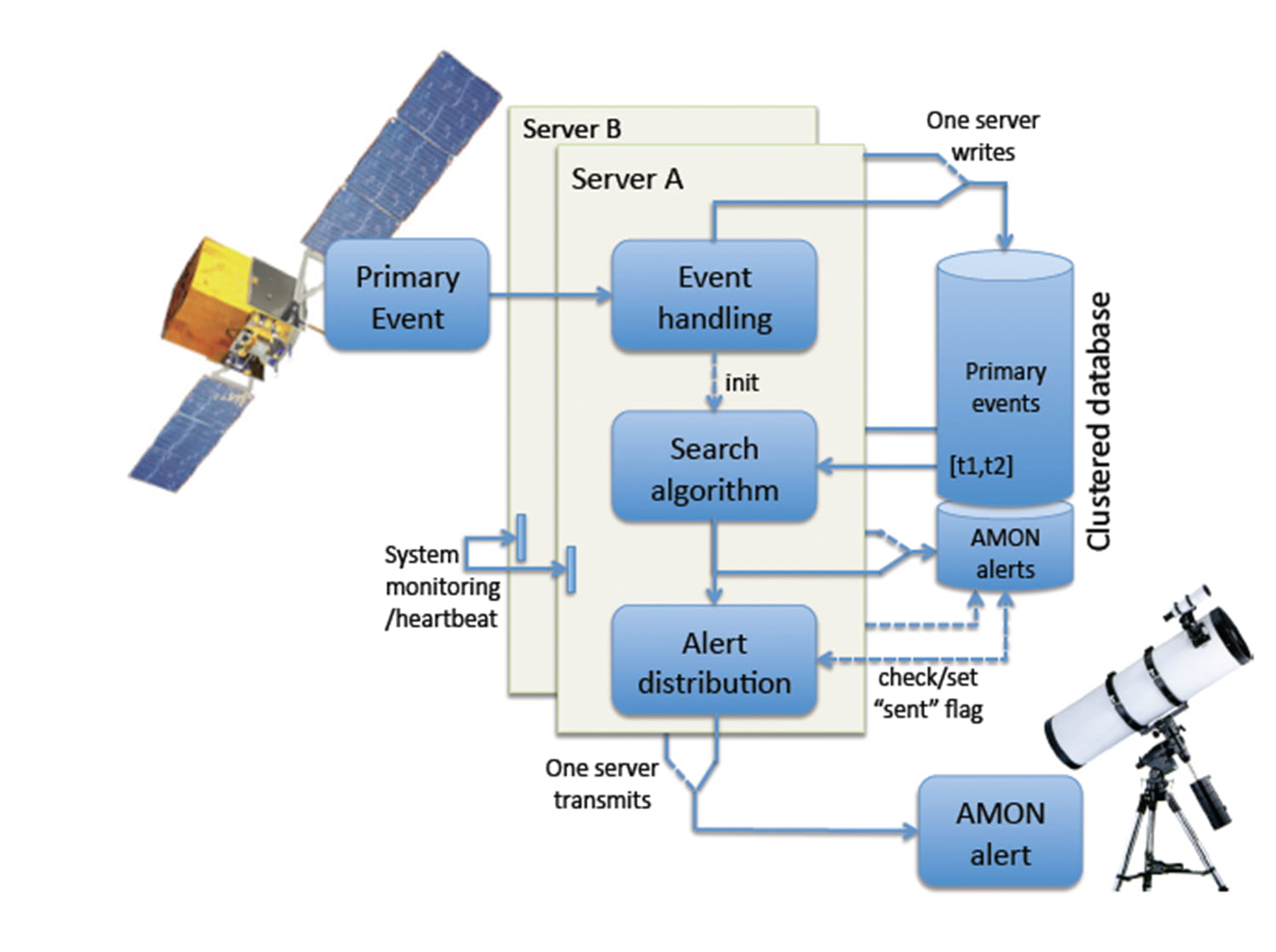
GRBs, and the mergers of super-massive black holes in the cores of galaxies and quasars are also likely sources of detectable gravitational waves. Our Center is engaged in observing GRBs, active galaxies, supernovae and clusters of galaxies, looking for strong-interaction protons and nuclei, weak-interaction neutrinos, electromagnetic radiation, and gravitational waves. Together we cover all four forces of nature. We have initiated and lead a specific multi-messenger observational program called the Astrophysical Multimessenger Observatory Network (AMON), which aims to utilize all four forces to detect sub-threshold signals from the above described cosmic sources. This multi-force approach to high energy astrophysics is a pioneering venture in which the one-dimensional electromagnetic spectrum of conventional astronomy is supplemented with three other windows to the Universe. The discovery potential is enormous.
Together with the Center for Fundamental Theory, the Center for Theoretical and Observational Cosmology and the Institute for Gravitation and the Cosmos, the synergy between our various specialties and the breadth of knowledge to be gained through collaborations provide exciting prospects for making breakthroughs in our understanding of the Cosmos.